Cellular Division Mitosis and Meiosis Biology Diagrams Plants have a life cycle characterized by alternation between two generations, haploid (gametophyte) and diploid (sporophyte), where each phase develops a multicellular body (1, 2).The gametophyte produces gametes—sperm (or pollen) and egg cells—and may be the dominant photosynthetic generation, as in liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. The BELL/KNOX and MADS-box transcription factors, which function in haploid-to-diploid transition and development in plants, are specifically expressed in the haploid and diploid, respectively, and are involved in the haploid-to-diploid transition in Galdieria, providing information on the missing link of the sexual life cycle evolution in
+Diploid+(2n)+Haploid+gametes+(n+%3D+23)+Ovum+(n)+Sperm.jpg)
Many organisms fall in between these extremes, however, with biphasic (or haploid-diploid) life cycles, promises to shed light on when transitions occur between haploid dominance and diploid dominance and the major life history features associated with these transitions. In the next section, we explore how organisms with different ploidy

Diploid Morphological Transition in ... Biology Diagrams
Transition from haploidy to diploidy Veronique Perrot*t:j:, Sophie Richerd* & Myriam Valero* interbreeding haploid and diploid individuals, that is, a popula
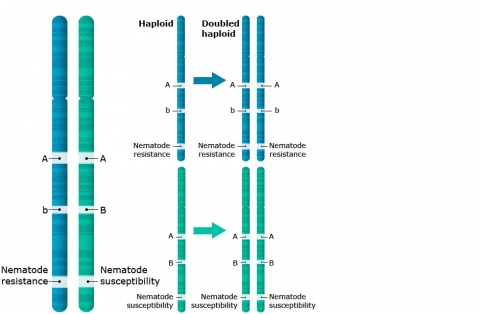
of haploid asexual females. Among plants, mitoses occur in both haploid and diploid phases, with the diploid phase predominating in ferns and seed plants. But polyploidy — having more than two sets of chromosomes — is very common among plants, and evidence is accumulating that all flowering plants have a polyploid history. In
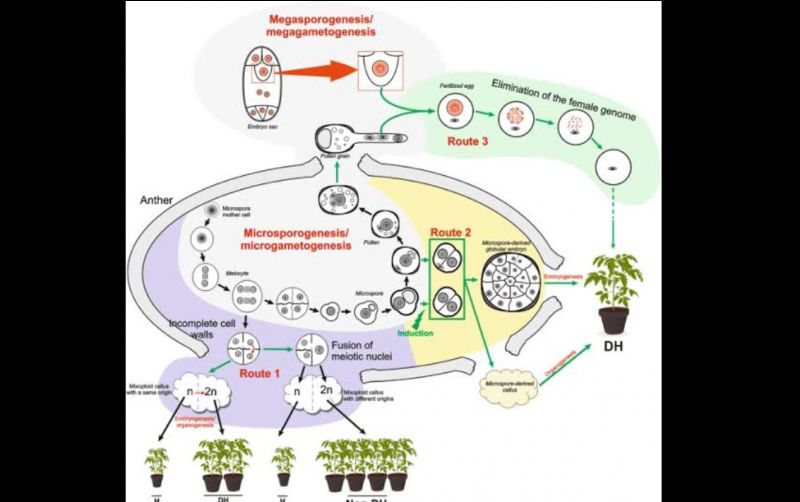
Chapter 11 Flashcards Biology Diagrams
Transition from haploidy to diploidy. June 1991; Nature 351(6324):315-7; DOI:10.1038/351315a0. To reveal how natural selection and genetic drift shape the evolution of haploid-diploid
:+after+meiosis.jpg)