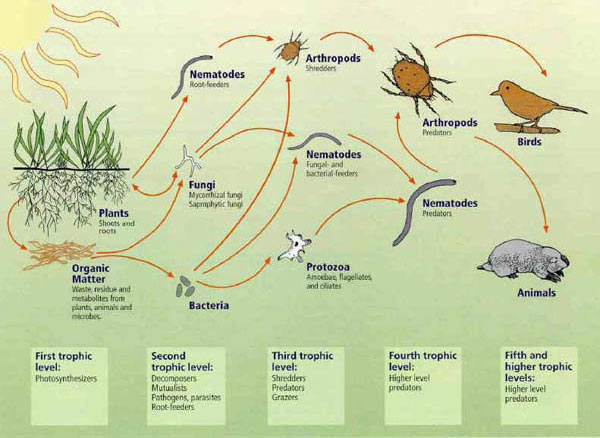
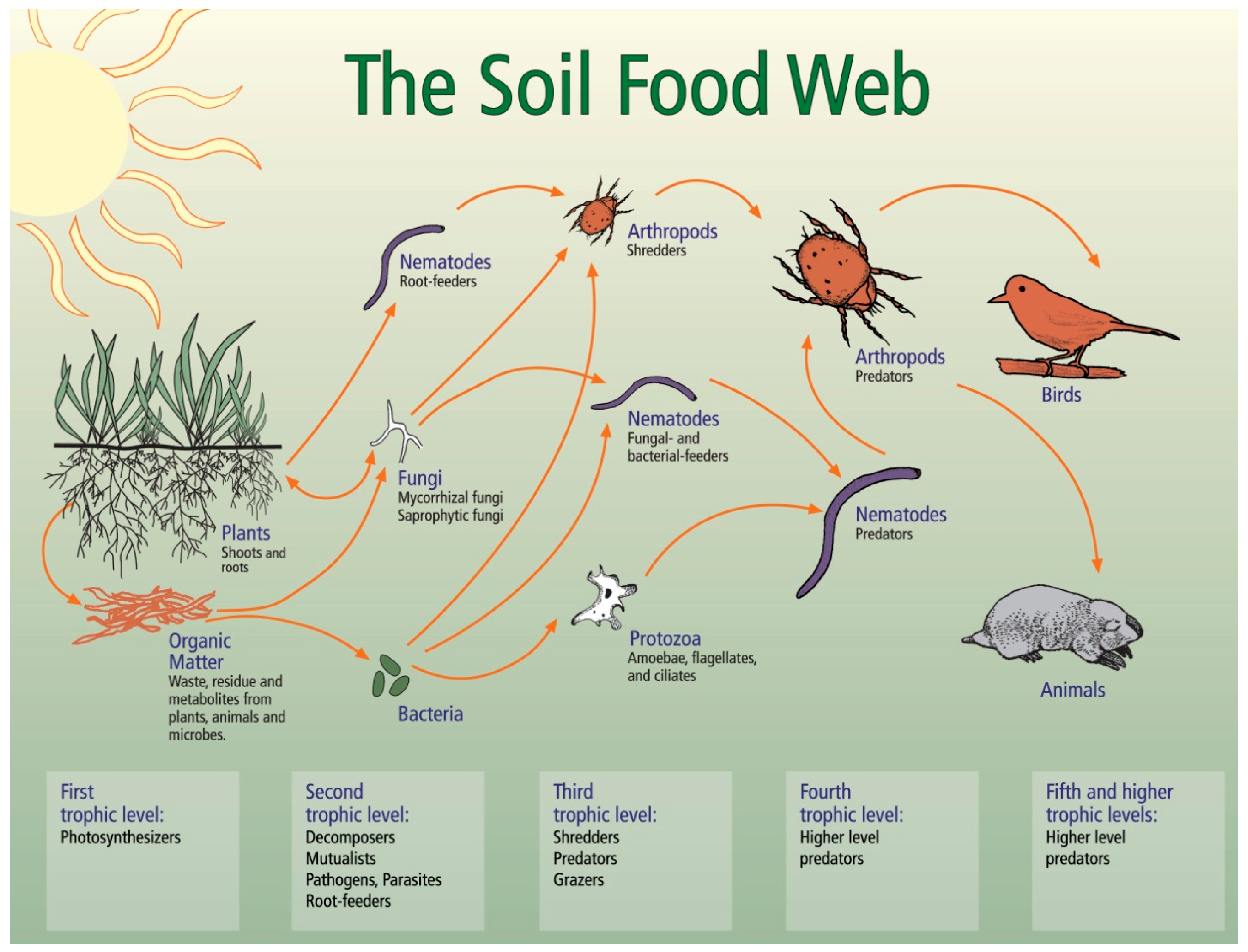
Soil Food Web Biology Diagrams The soil food web is the community of organisms living all or part of their lives in the soil. It describes a complex living system in the soil and how it interacts with the environment, plants, and animals. At the end of the food chain, decomposers such as bacteria and fungi break down dead plant and animal material into simple nutrients Detritus food chain: The detritus food chain includes different species of organisms and plants like algae, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, mites, insects, worms and so on. The detritus food chain begins with dead organic material. The food energy passes into decomposers and detritivores, which are further eaten by smaller organisms like carnivores.
Every living plant and animal must have energy to survive. Plants rely on the soil, water, and the sun for energy. Animals rely on plants as well as other animals for energy. In an ecosystem, plants and animals all rely on each other to live. Scientists sometimes describe this dependence using a food chain or a food web. Food Chain
18.20: Food Chains and Food Webs Biology Diagrams
The scientific understanding of a food chain is more precise than in its everyday usage. In ecology, a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass: primary producers, primary consumers, and higher-level consumers are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. There is a single path through the chain. Food chain, its types and eg. are briefly mentioned in the article below. A food chain is like a line that shows who eats whom in nature, as animals and plants are linked because they eat each other. Food chain, its types and eg. are briefly mentioned in the article below. the decomposers act on their bodies and return all the various

The energy flow from one level to another level in a food chain gives the trophic level of an ecosystem. The producers come at first trophic level followed by herbivores (primary consumers), then small carnivores (secondary consumers) and large carnivores (tertiary consumers) occupy the fourth trophic level. Conclusion - Ecosystem and its

Definition, Parts, Types, and Examples Biology Diagrams
Food chains also display what happens when a problem occurs and a producer or consumer is lost. Entire communities can collapse. **Food chains can help scientists learn more about ecosystems and how to help them stay balanced.** Depending on the food chain you are examining, the same organism can be considered to be at more than one trophic
